Different Types OF Businesses:
Corporate Business :-
A Corporate is a business structure or a legal form of organization.
It has a separate legal identity distinct from its owners. The owners of a corporate are called as shareholders. In most of the countries, the formation of a corporate involves an extensive legal work and fulfillment of strict legal criteria.
This is due to the principle of corporate veil or the separate legal person status of a corporate from its owners, some of whom try to take undue advantage of this legal provision. Corporate raises the capital or funds by selling its stocks to the individuals or other legal entities. A corporate has a board of directors selected by the shareholders.
Industrial Business :-
It could mean industrial land or an area which refers to an area which has factories. They are generally on the outskirts of cities.
Basically it includes something relating to industry. Some of the dictionary meanings of “industrial” used as adjectives are Something resulting from or relating to industry.
For example, industrial development. Somebody working in or required to be employed in any industry, for example, industrial workers.
Partnership Business :-
A partnership is a formal arrangement by two or more parties to manage and operate a business and share its profits.
There are several types of partnership arrangements. In particular, in a partnership business, all partners share liabilities and profits equally, while in others, partners may have limited liability.
There also is the so-called "silent partner," in which one party is not involved in the day-to-day operations of the business.
Service Business :-
Business services are a recognizable subset of economic services, and share their characteristics.
The essential difference is that businesses are concerned about the building of service systems in order to deliver value to their customers and to act in the roles of service provider and service consumer.
Ownership implied tangible possession of an object that had been acquired through purchase, barter or gift from the producer or previous owner and was legally identifiable as the property of the current owner.
Manufacturing Business :-
A manufacturing business is any business that uses components, parts or raw materials to make a finished good. These finished goods can be sold directly to consumers or to other manufacturing businesses that use them for making a different product.
Manufacturing businesses in today's world are normally comprised of machines, robots, computers, and humans that all work in a specific manner to create a product.
Manufacturing plants often use an assembly line, which is a process where a product is put together in sequence from one work station to the next. By moving the product down an assembly line, the finished good can be put together quicker with less manual labor.
It's important to note that some industries refer to the manufacturing process as fabrication and All Goods/Products.
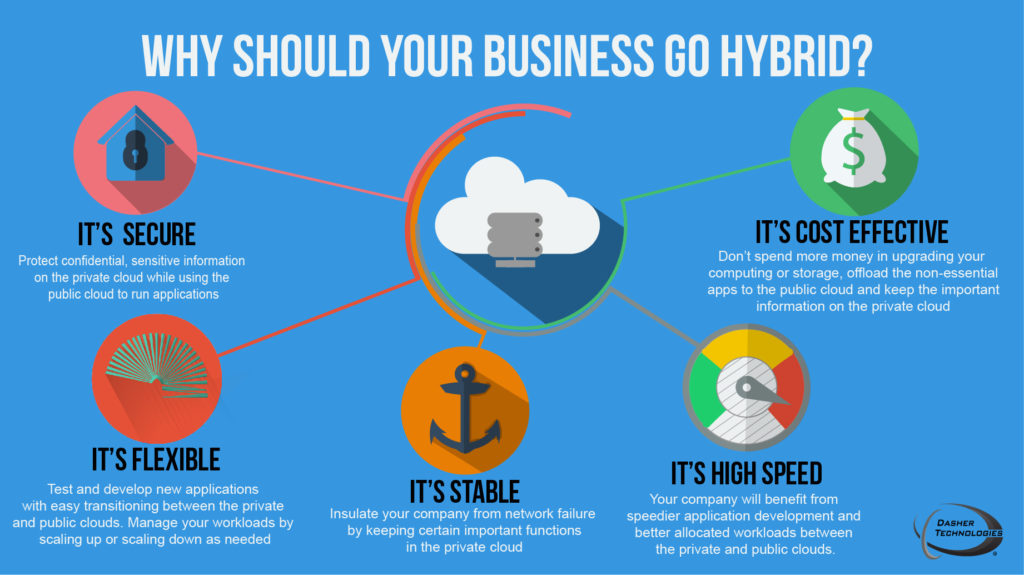
Hybrid Business :-
Hybrid is something we make by combining two different elements or the offspring of two plants or animals.
The word may also refer to something of mixed character that consists of two different elements. For example, jungle is a hybrid of house and reggae music, while a mule is a horse-donkey cross.
We refer to cars that use both electricity and gasoline as hybrids. In fact, we use the term to describe many things that consist of a combination of at least two elements. A hybrid business is a company that has both an Internet-front end as well as its bricks and mortar premises. In other words, a business with a strong online presence and also warehouses and physical shops.
Merchandising Business :-
A merchandising business, sometimes called merchandisers, is one of the most common types of businesses we interact with daily. It is a business that purchases finished products and resells them to consumers.
Think of the last time you went shopping for food, household items, or personal supplies. You were likely in a merchandising business. That store had purchased the items wholesale from a distributor or a manufacturer and made it available to you.
While the store may have been required to purchase in large quantities, they offer the product to you in a small, personal-use size.
For instance, a wholesaler may offer deodorant to a merchandising business at a large discount, but they will likely require the store to purchase hundreds, even thousands, of units to qualify for a discount. The store then offers the deodorant to you at the retail price and allows you to purchase one container.
The difference in the amount you paid the store and the store paid the wholesaler is the store's profit. The profit allows the store to stay in business and offer you products in the future.